Measurable Properties of Gases
Measurable Properties of Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Thermal Energy, Intermolecular Forces versus Thermal Energy, Measurement of Pressure Using Barometer & Measurement of Pressure Using Manometer etc.
Important Questions on Measurable Properties of Gases
The temperature increases, the intermolecular forces of the gas molecules
atmosphere = torr of . Here is
A desiccator of internal volume of and containing nitrogen at pressure is partially evacuated to a final pressure of , while the temperature remains constant. What is the volume of the gas in litre at this stage?
The pressure exerted by the gas is due to
Kinetic energy of a gas
Which description fits best for a gas?
A sample of gas is collected over water at at a barometric pressure of (vapour pressure of water at is ). The partial pressure of gas in the sample collected is
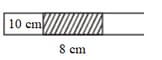
A 10 cm column of air is trapped by a column of Hg, 8 cm long, in a capillary tube horizontally fixed as shown below, at 1 atm pressure.
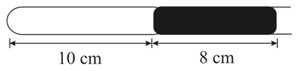
What is the pressure of air when the tube is held horizontally at with the open end up?
A 10 cm column of air is trapped by an 8 cm long column of Hg in a capillary tube horizontally fixed as shown in the figure at 1 atm pressure.The pressure of air measured when a tube is held vertically with the open end up is:
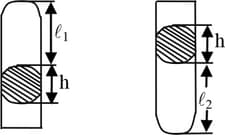
Air separated from the atmosphere by a column of mercury of length is present in a narrow cylindrical soldered at one end. When the tube is placed horizontally the air occupies a volume . When it is set vertically with its open end upwards the volume of the air is . The atmospheric pressure during the experiment is . Find .
What would be the height of a barometer column for one standard atmosphere, if water were used instead of mercury?
A bubble of gas released at the bottom of a lake increases to eight times its original volume when it reaches the surface. Assuming that atmospheric pressure is equivalent to the pressure exerted by a column of water, 10 m height, the depth of the lake is:
An air column closed in a tube sealed at one end by a column having height . When the tube is placed with open ends down, the height of the air column is . If the tube is turned so that its open end is at the top, the height of the air column is . What is the atmospheric pressure -
A gas is present in a cylinder fitted with movable piston. Above and below of the piston there is an equal number of moles of gas. The volume above is two times the volume below at a temperature of . At what temperature will the volume above be four times the volume below-
At constant volume, for a fixed number of moles of a gas, the pressure of the gas increases with rise of temperature due to
When a capillary tube of diameter is dipped in a liquid having a density of then the height of the liquid in the capillary tube rises to . The surface tension of the liquid is
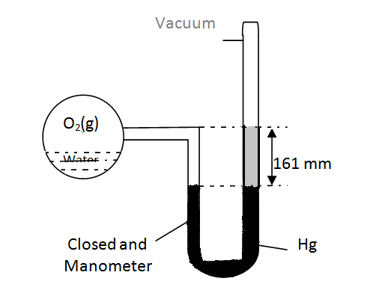
A bulb of constant volume is attached to a manometer tube open at another end as shown in the figure. The manometer is filled with a liquid of density that of mercury. Initially, was .
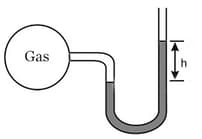
Through a small hole in the bulb, gas is leaked. Assuming, pressure decreases as , if the value of is after . What is the value of ?
A bulb that has constant volume is attached to a manometer tube open at the other end, as shown in the diagram. The manometer is filled with a liquid of density that of mercury. Initially, was 228 cm.
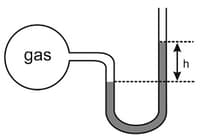
Through a small hole in the bulb, gas leaked assuming pressure decreases as . If the value of is after . What is the value of ?
[Use: ln and density of ].
An open manometer attached to a flask containing ammonia gas have no difference in mercury level initially as shown in diagram. After sparking into the flask, ammonia is partially dissociated as . Now it have difference of in mercury level in two columns, what is partial pressure of at equilibrium ?
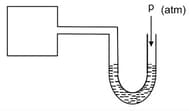
The system shown in the diagram is at equilibrium at And volume of the bulb is 150 mL. At this temperature, the vapor pressure of water is 28 millimeters of mercury. If,the bulb contains 0.001 mol of O2 (g), volume of the liquid water is approximately.